1. Power aware Routing Protocol for Manets based on Swarm Algorithm
Introduction ANET comprises of a few portable remote hubs that speak with one another through immediate or circuitous correspondence joins. Hubs inside these systems demonstration like switches. The nonattendance of foundation and the portability of these hubs create a huge test to steer calculations in such systems. A node in the MANET is controlled on battery. Minimizing correspondence related force utilization is an essential planning routing protocol. Routing protocol assumes huge part in deciding system execution.
The ad hoc on demand distance vector routing convention is a responsive unicast steering convention for versatile impromptu systems. As a receptive steering convention, AODV just needs to keep up the directing data about the dynamic ways. In AODV, the steering data is kept up in the directing tables at all the hubs. Each portable hub keeps a next bounce steering table, which contains the destinations to which it as of now has a course. A directing table passage terminates in the event that it has not been utilized or reactivated for a pre specified close time On demand tree based routing protocol used to combining the levels of node by node by using the algorithm is Tree based optimized flooding .Which can be used to increase the connectivity and extending the network lifetime.
routing protocol is a table driven directing convention where all hubs are obliged to have complete information about the system and therefore directing tables are intermittently updated. On the other hand, reactive conventions set up courses on requests. At whatever point a hub obliges a course to a particular destination, it begins course setup method. Course revelation prepares more often than not comprises of television a course demand message all through the network. Hybrid routing conventions tries to address the issue in both receptive and proactive by consolidating highlights from both responsive and proactive conventions into a crossover convention. A case of crossover directing convention is zone routing. The primary downside of hybrid routing convention is the high asset use.
2. II.
3. Related Works
A routing protocol is a development process that tries to improve system performance. In AODV acquainted with tackle directing issue. AODV is a standout amongst the most well known traditional directing conventions for portable specially appointed systems. At whatever point a hub needs to send information to a destination, and it doesn't have the legitimate course to destination, it telecasts a Route Request (RREQ) message to discover the destination. After accepting RREQ, Route Replay (RREP) message is sent back to the source. AODV in its unique structure utilizes hi message to intermittently redesign its neighbour hubs accessibility. Join breakage could be distinguished in the event that unsuccessful parcel transmission happens or missing hi message. If there should be an occurrence of connection disappointment the hub send back a Route Error (RERR) to the source to scan for new course.
RFD is a subset of swarm knowledge. Actualizing the RFD calculation in impromptu steering conventions gives numerous preferences. As a matter of first importance, as there are no retrogressive specialists in the RFD calculation, it will diminish the aggregate number of control bundles in the system. Another preference is the straight forwardness of the calculation, particularly it relates heights to hubs instead of connections. As for the most part the quantity of the hubs is typically not exactly the number of connections in a system. This minimizes the asset use.
The hybrid swarm algorithm has been proposed for routing problems in MANETs. This protocol has higher bundle overheads which more often than not bring about devouring higher battery power, For this power aware routing protocol is developed.
Distinctive power mindful routing conventions have been proposed to take care of steering issues in specially appointed system .Probabilistic examination is utilized to demonstrate the impact of multi-client obstruction with and without appropriate force control of system execution. The creators ponder the impact of obstruction, force control and diverse sending technique on system lifetime. Two systems for parcel sending present by the creators, power controlled nearest forward (PCN) and system lifetime expanding PCN (E-PCN). These systems attempt to expand the system lifetime.
4. III.
5. Motivation
The various characteristics of MANETs, like dynamic and changing topology, foundation less remote correspondence media, adds additional manysided quality to routing protocol with a specific end goal to locate the ideal way to satisfactory QoS in the middle of source and destination hubs. Move process in such a method is tests matter specially if how much offered interfaces is limited. The problem connected with acquiring a well balanced means taking into consideration interconnection characteristics involving hubs obliges re-examination.
Giving information bundles the capacity to gather course data, and join with control, parcel during the time spent discovering an ideal way could upgrade system execution. Subsequently, this will issue them the capacity to move and quest for their own particular destinations.
IV.
6. Problem Statement
The hybrid ACO and RFD standard protocol have higher packet overheads which for the most part results in consuming higher battery power. To reduce the higher battery power , power aware routing protocol is developed based on Swarm algorithm.
V.
7. Problem Formulation
The hybrid ACO and RFD standard protocol have higher packet overheads which for the most part results in consuming higher battery power.
To reduce the higher battery power, power aware routing protocol is developed based on Swarm algorithm without the partition of routing data, Where energy trademark is changed over to altitude parameters. Packets are sent by remaining power in hubs. The convention moreover outputs for the briefest and non-congested approach to destination. This will reduce the quantity of retransmission in the system which saves power.
8. VI.
9. Mathematical Model
In the RFD algorithm route will be discovered using following equations For source node Alts(j) = Alts(j) -µ(Alts(j) -Broadalt), µ Ñ?"[0,1] For destination node Altd(j) = minil?V(altd(l)) -gradient *( minil?V(altd(l))altd(i))
Average time to send a packet is
Dk(t) = ?Dk(t-1)+(1-?)Nk(t), ? Ñ?"[0,1]In RFD Hello message is utilized to find neighbour hubs and to propagate data around the system.
Altd(j) = Altd(j) -µ(altd(j) -Halt d), µ Ñ?"[0,1]The measure of disintegration is relative to remaining battery control in the hub and the height angle between the hub itself and the selected sending hub.
Ed(j)=? * Pr/ P(Altd(j) -Altd(k)) a) River Formation Dynamics Algorithm Year ( ) With a specific end goal to assess the execution of our proposed convention, the protocol executed utilizing OMNet++ as simulation programming. For the AODV convention, the INETMANET add-on bundle of the OMNet++ is utilized. In a scope of tests, proposed routing protocol has been compare with AODV.
10. a) Results
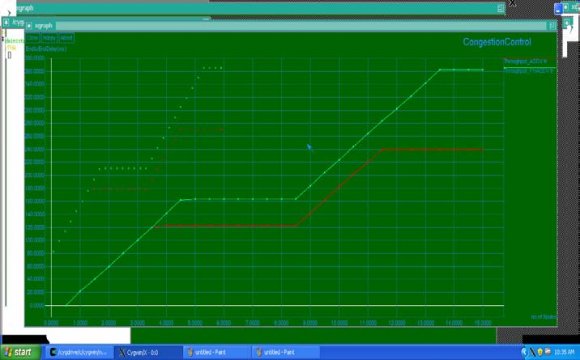
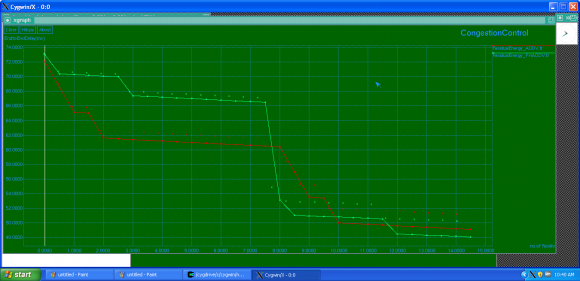
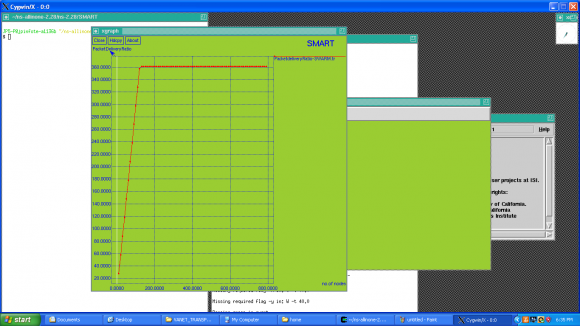
Fig 1 shows throughput of the proposed convention with AODV protocol for diverse estimations of hubs speeds. It obviously represents that smart routing protocol accomplishes higher throughput than AODV protocol under RWP and GM portability. As the pace of hubs expands, the likelihood of connection break builds, this thusly, diminishes the system throughput. We can like wise watch that both conventions throughputs get to lower at rapid.
11. Conclusion
In this work, Swarm algorithm based SMART protocol we have been. The proposed protocol is power mindful where packets are directed through less congested range of the system to save power. In the mean time the convention detects the remaining battery power of the hubs and inclines towards hubs with higher battery level. The convention is taking into account RFD swarm algorithm. This algorithm is developed from